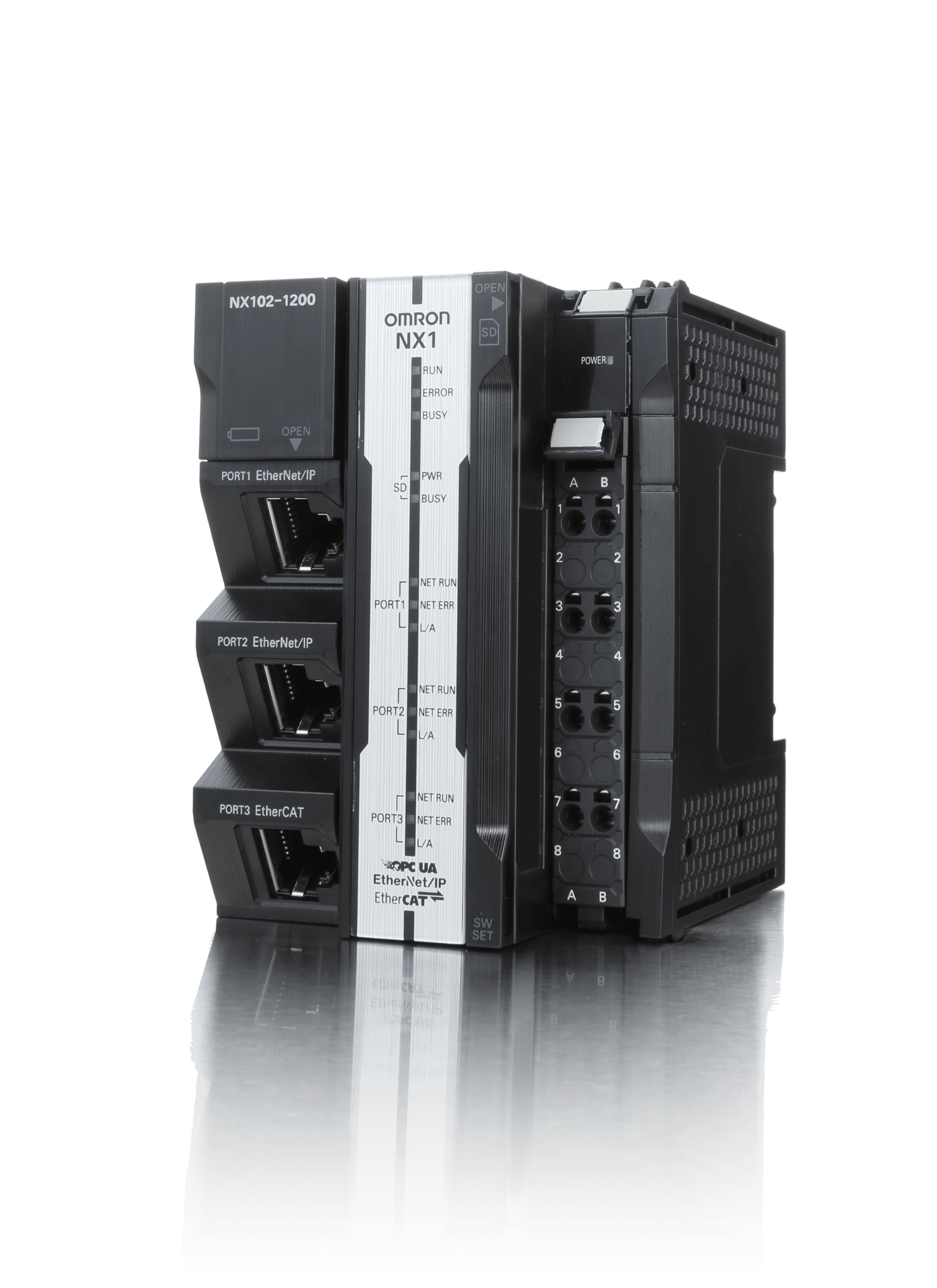
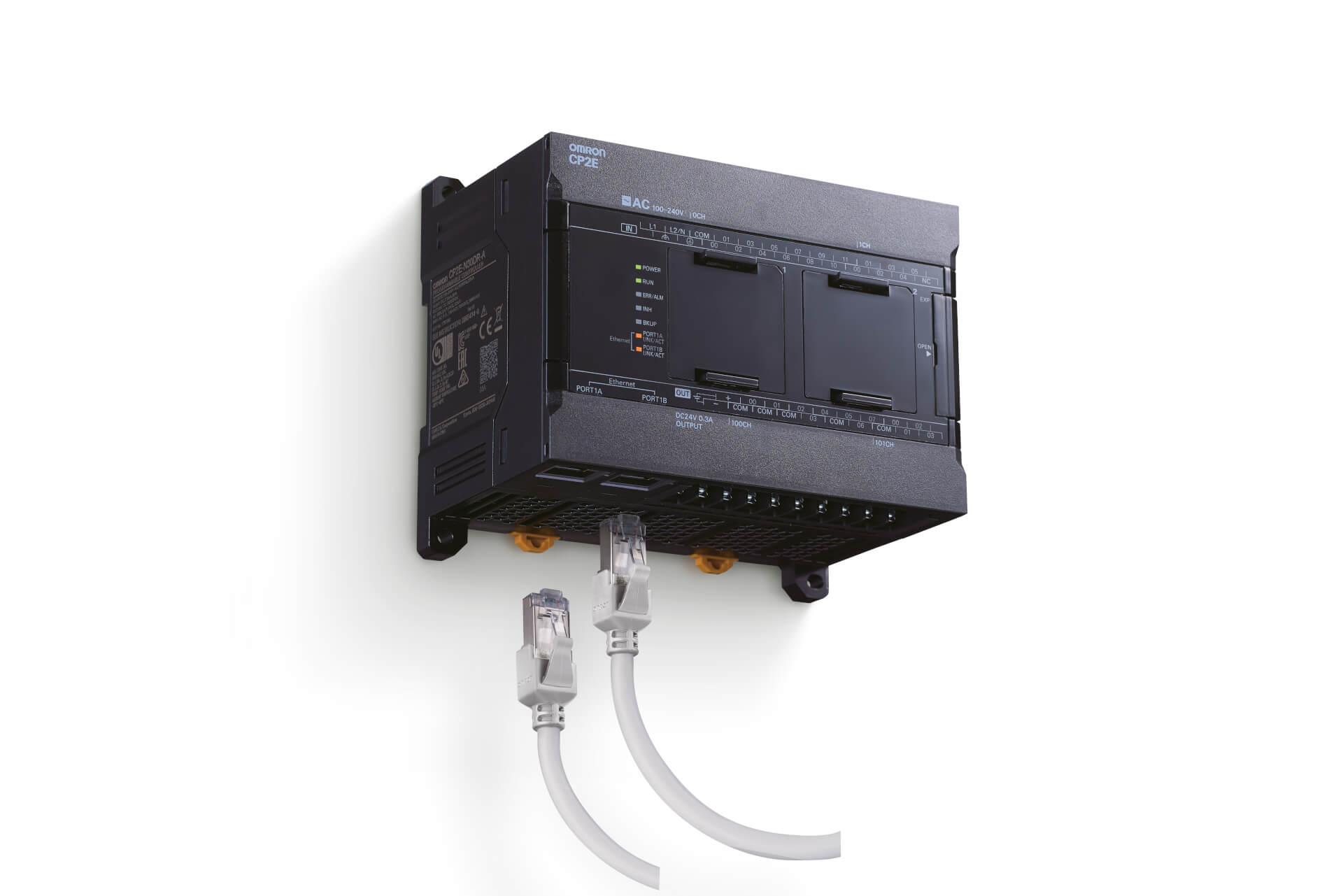
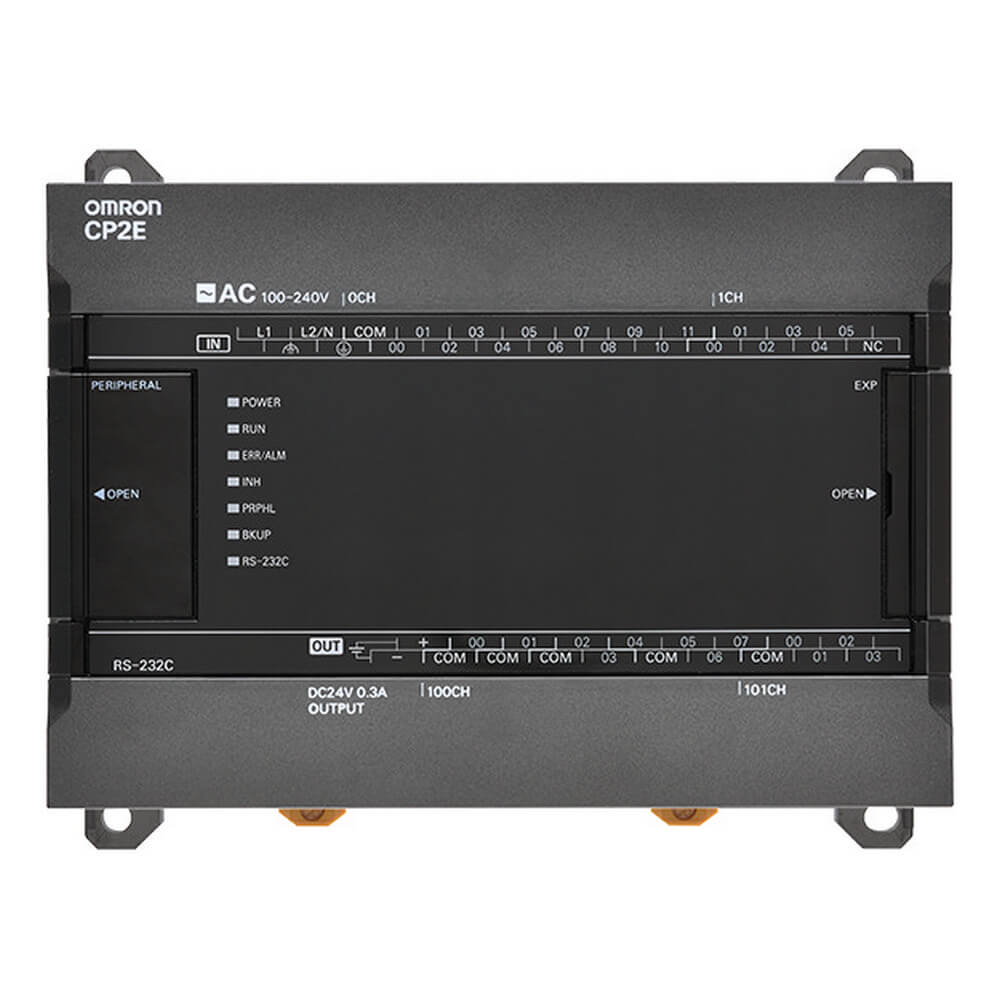
Programmable logic controllers (PLC)
A Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is a specialized hadware designed to manage control tasks in industrial settings.
A PLC is a special kind of digital computer that plays a crucial role in industrial automation. It has a CPU that runs the control program and manages other components.
Ever peeked inside a control cabinet on a factory floor?
If so, you've likely seen PLCs at work. Often called the brains of a production line, PLCs are vital for industrial automation. Engineers design, program, and set up PLC systems to fit the needs of specific automation tasks. PLCs control and monitor machinery and processes, boosting productivity, reliability, and safety.
If you haven't looked inside a control cabinet yet, keep reading to learn about the amazing technology powering today's industries.
| CJ2 | CP2E | CP1L | CP1E | CP1H | CS1D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
| Modular | Compact | Compact | Compact | Compact | Rack | |
| 2560 | 180 | 180 | 180 | 320 | 960 to 5120 | |
| 4 axes PTO I/O line driver | Up to 4 axes linear interpolation and PWM | 2 axes PTO I/O and PWM | 2 axes PTO I/O and PWM | 4 axes PTO I/O line driver | - | |
| 5 to 400K steps | 4 to 10K steps | 10K steps | 2 or 8K steps | 20K steps | 10 to 250K Steps | |
| 64 to 832K Words | 4 to 16K words | 32K words | 2 or 8K words | 32K words | 64 to 448K Words | |
| CompoNet Controller Link DeviceNet EtherNet EtherNet/IP ModBus TCP ModBus RTU PROFIBUS-DP PROFINET CAN (freely configurable) | EtherNet ModBus TCP ModBus RTU Serial | EtherNet ModBus TCP ModBus RTU Serial | ModBus RTU Serial | CompoNet Controller Link DeviceNet EtherNet EtherNet/IP ModBus TCP ModBus RTU PROFIBUS-DP PROFINET CAN (freely configurable) | Controller Link (duplex/optical ring) DeviceNet EtherNet EtherNet/IP | |
| Function Block Ladder programming Structured Text programming with structures and arrays | Function Block Ladder programming | Function Block Ladder programming | Ladder programming | Function Block Ladder programming | - | |
| CJ2 | CP2E | CP1L | CP1E | CP1H | CS1D |
Contact us
Need assistance?
We’re here to help! Reach out, and our specialists will assist you in finding the best solution for your business.
Contact me Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC)

Thank you for submitting your request. We will come back to you as soon as possible.
We are experiencing technical difficulties. Your form submission has not been successful. Please accept our apologies and try again later. Details: [details]
DownloadQuotation for Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC)
By completing this form you can request a quotation. Your personal details will be handled confidentially.

Thank you for requesting a quotation. We will provide you with the required information as soon as possible.
We are experiencing technical difficulties. Your form submission has not been successful. Please accept our apologies and try again later. Details: [details]
DownloadTechnology
What Is a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC)?
How does a PLC work?
In industrial automation, a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is crucial for managing complex tasks. But how exactly does a PLC function?
How PLCs adapt to industrial needs
Sensor input to machine operation
Equipment Control
Connecting Industry Tools
Solutions
OMRON's line of PLCs
Explore our range of programmable logic controllers, PLC solutions designed to excel in complex industrial automation settings.
We offer a comprehensive range of PLC solutions, combining precision, performance, and reliability to meet diverse industrial automation needs.
- Compact PLCs offering scalable options
- Modular Controllers for complex, high-performance applications
- Dual-Redundant PLC System ensures never-fail control for critical applications
- Controllers for synchronized device control, IoT connectivity, and advanced motion control
- PLC's with AI for real-time learning and predictive maintenance.
- Sysmac Studio for an all-in-one setup for programming PLCs
- Additional for setup customization
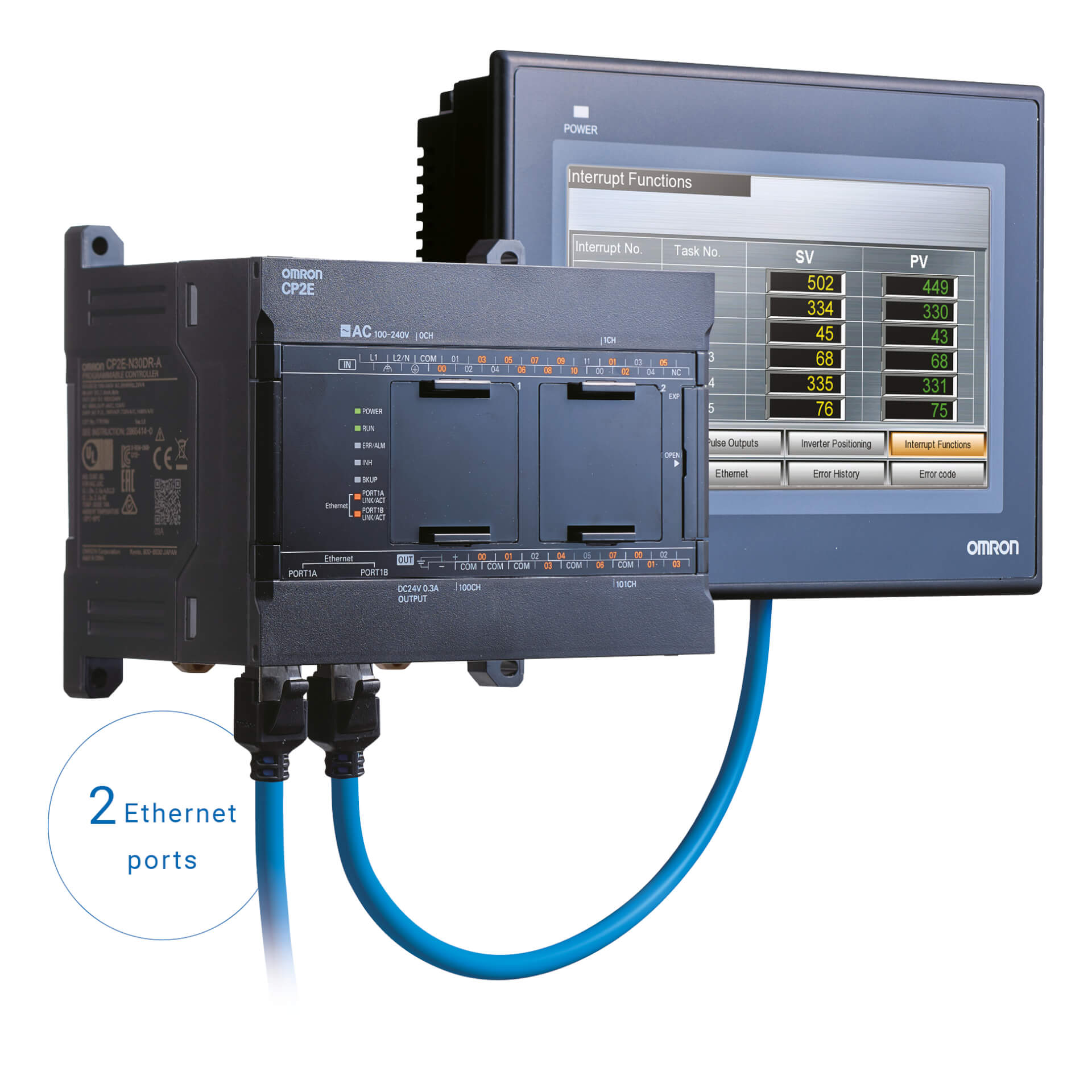
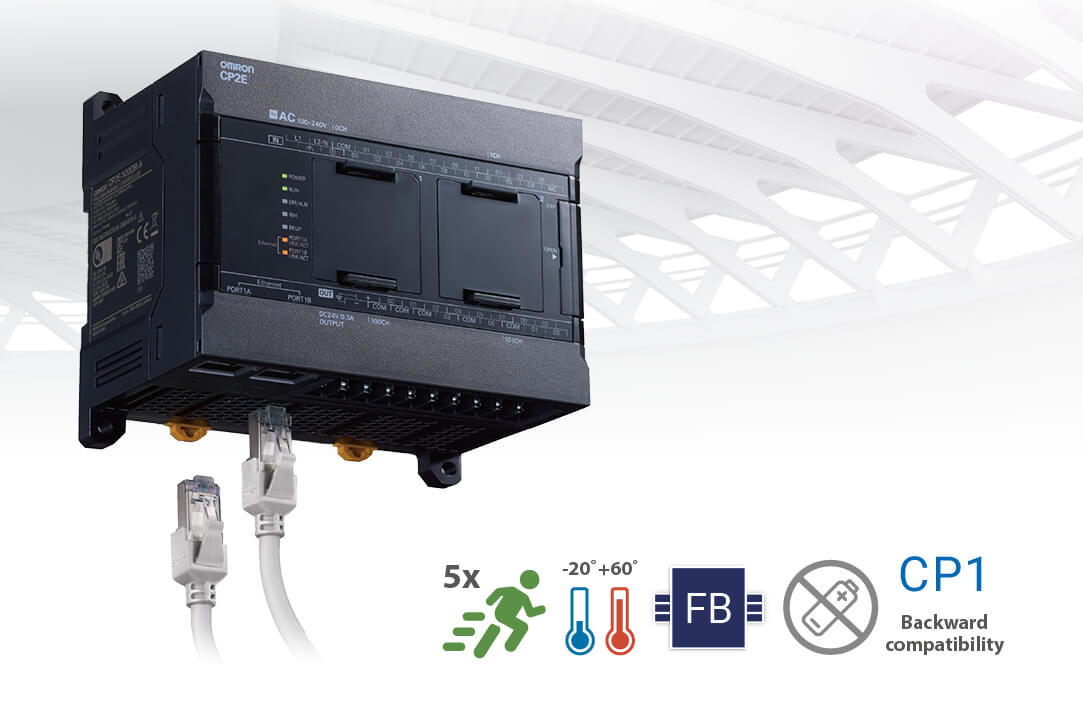
CP Family of compact PLCs
CJ2 Modular Controllers
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) have evolved over time into more advanced systems known as Machine Automation Controllers (MACs)
Sysmac Studio for PLC
PLC advantages and disadvantages
- Flexibility in programming and easy adaptability to different control requirements and applications
- Reliable operation even in challenging conditions
- A wide range of PLC options on the market, each tailored to specific needs
- Scalability to meet changing automation needs
- Real-time control for quick response times and precise coordination of machinery and processes
- Built-in diagnostics and monitoring features simplify troubleshooting and maintenance tasks
- Seamless integration with other automation components and systems facilitates data exchange and coordination
- Support for the implementation of safety functions, enhancing workplace safety
- Collecting and logging data for analysis, enabling performance monitoring, predictive maintenance, and process optimization
- Better long-term value due to lower maintenance costs and increased system flexibility, making them a cost-effective choice over time
- Specialized knowledge required for programming
- Higher initial cost compared to other traditional control systems
- If the system isn't protected, it becomes more vulnerable to cyber threats
- Different PLC brands may use proprietary programming languages or software
What applications use PLC?
PLCs can be implemented basically in any automation and machine control application. Let’s look at a bottling line in a beverage factory as an example. Here are a few of the tasks a PLC can perform:
Control speed and direction
Monitoring and Measuring operations
Inspection and Quality Control
Managing the Packaging Process
Overseeing Production Line Operations
Programmable logic controllers hardware and programming
What programming language is used to program a PLC?
PLC Software Integration for All Series with SCADA Systems
- advanced monitoring
- data acquisition
- a user-friendly interface for operators to control machines efficiently, eliminating the need for manual button pressing or switch manipulation.
What do I need to consider when choosing a PLC?
- Assess the system size and the required response rate for your process. Choose a PLC with a CPU speed that matches your application's demands.
- Determine the necessary memory capacity for your program. Consider if an external memory card will be required to accommodate program size.
- Decide if any level of redundancy is necessary for your application to ensure uninterrupted operation in case of system failure.
- Count the number of devices your PLC needs to control or monitor. Consider if there's a need to work with external or remote I/O interfaces.
- Identify the devices your PLC must communicate with and the communication protocols they use. Ensure compatibility with these protocols.
- Determine if your system is being built from scratch or if it needs to interface with existing hardware and software. Ensure compatibility with existing components.
- Evaluate whether the system can be easily scaled up or down to accommodate changes in your process or system requirements.
- Consider the environmental conditions your PLC will be exposed to. Assess if it needs special features such as conformal coated components for harsh environments.
- Determine if your application requires unique actions, such as motion control, robotics, or safety features. Choose a PLC that supports these functionalities.
- Assess the expected uptime requirements of your system. If it needs to run continuously for extended periods, select a PLC known for its reliability.
- Define your budget and consider the collective costs, including hardware, software licenses, programming, installation, ease of integration with existing systems, maintenance, and future upgrades.
Key Takeaways about PLC's
- PLCs, or Programmable Logic Controllers, are the cornerstone of industrial automation, and thrive in challenging environments by offering a robust platform for precise control. These systems stand out for their consistent, high-quality performance, durable construction, and flexible functionalities and can be used in a wide range of applications.
- Selecting the right PLC demands a careful analysis of your specific automation needs, taking into account key factors such as the processing speed of the CPU, the storage capacity for program and data handling, and the system's compatibility with existing machinery and software.

Finished seals in less than 10 seconds: Robotics Integrated Controller ensures harmonious control
Trelleborg Livorno has updated a robotic cell for the finishing of polyurethane gaskets for the sustainable wind energy market. The cornerstone of the solution is OMRON's Robotics Integrated Controller that ensures integration and synchronization of all automation components, including robots, logic, motion, safety and user interface.

Watch video on an innovative anti-sloshing solution for soup and ready meal packaging
Italian Pack and OMRON have joined forces to introduce Argo, an automatic tray sealing machine equipped with an innovative anti-sloshing system

Picomel looks to the future with a visionary production line
Vertical factory saves space and energy while reducing waste
We’re Here to Help
Got a question? Our specialists are ready to assist you every step of the way.
Contact me Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC)

Thank you for submitting your request. We will come back to you as soon as possible.
We are experiencing technical difficulties. Your form submission has not been successful. Please accept our apologies and try again later. Details: [details]
DownloadQuotation for Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC)
By completing this form you can request a quotation. Your personal details will be handled confidentially.

Thank you for requesting a quotation. We will provide you with the required information as soon as possible.
We are experiencing technical difficulties. Your form submission has not been successful. Please accept our apologies and try again later. Details: [details]
Download